Headlight Compatibility Checker
Check Your Headlight Compatibility
Answer a few questions to determine if you can directly replace your halogen headlights with LED bulbs.
Compatibility Results
Ever stared at a box of bright LED modules and wondered if you could just pull out the old halogen bulbs and drop the new ones in? The short answer is: it’s not that simple. Swapping halogen bulbs for LED headlights involves more than a twist‑and‑turn; you’ve got to consider fit, wiring, CANbus communication, and legal requirements. Below we break down every angle so you can decide whether a straight swap will work for your car or if you need extra parts and tweaks.
What a Halogen Bulb Actually Is
Halogen bulb is a type of incandescent lamp that uses a tungsten filament surrounded by halogen gas to boost efficiency and lifespan. When you turn on the headlights, the car’s ECU (electronic control unit) sends a 12‑volt supply to the filament, causing it to glow and emit roughly 1,000‑1,500 lumens for a typical H7 or H4 lamp. The filament is housed in a glass envelope, and the heat generated is part of the design-halogen bulbs need high temperatures to maintain the halogen cycle that protects the filament.
How LED Headlights Differ
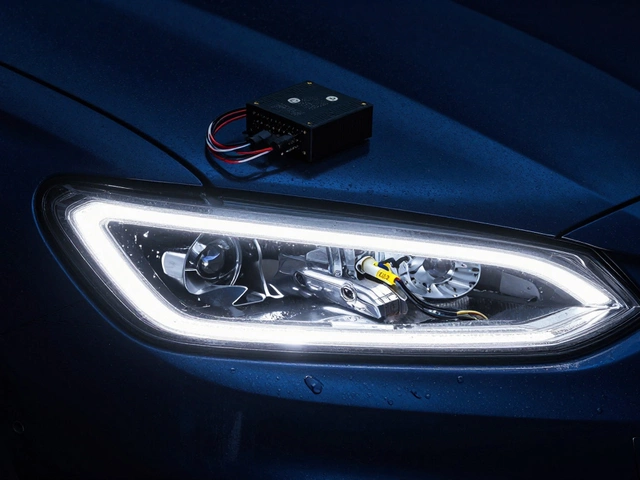
LED headlights are semiconductor light sources that convert electricity directly into light. They produce a focused, bright beam with far fewer watts (often 15‑30 W) while delivering 2,500‑4,000 lumens depending on the module. LEDs also emit a specific color temperature measured in Kelvin (usually 5,000‑6,500 K) that feels “daylight‑white.” Because LEDs run cooler than halogens, they require a heat‑sink and sometimes a dedicated driver circuit to regulate voltage.
Fit and Form Factor: Can You Screw an LED into a Halogen Socket?
Many LED replacement kits are designed to match the physical base of common halogen sizes-H7, H4, H1, H3, and HB3. If the base lines up, the bulb will sit in the housing without modification. However, a true “swap” depends on three things:
- Base Compatibility - The LED’s base must match the vehicle’s socket (e.g., H7‑LED into an H7‑halogen socket).
- Space Inside the Housing - LED modules can be longer or bulkier due to heat‑sink fins, potentially touching the reflector or projector lens.
- Electrical Load - LEDs draw less current, so the car’s lighting circuit may think a bulb has failed.
If any of these points fails, you’ll need adapters, a different LED model, or a custom mount.
Wiring, CANbus, and the ECU: Why the Dashboard Might Flash
Modern cars use a CANbus (Controller Area Network) to monitor the status of each headlight. The system expects a certain resistance range from a halogen filament (about 5-8 Ω). When an LED draws far less resistance (often under 1 Ω), the ECU registers a “bulb‑out” condition and triggers a warning light.
There are three common ways to solve this:
- Load Resistors - Add a resistor that mimics the halogen’s resistance, usually a 6 Ω, 30 W part placed near the LED.
- CANbus Decoders - Small modules that send a fake “bulb‑present” signal to the ECU, eliminating the warning.
- ECU Re‑programming - On some tunable vehicles, a dealership can adjust the software to accept LED loads.
Choosing the right approach depends on your car’s make, model year, and how comfortable you are with electrical work.
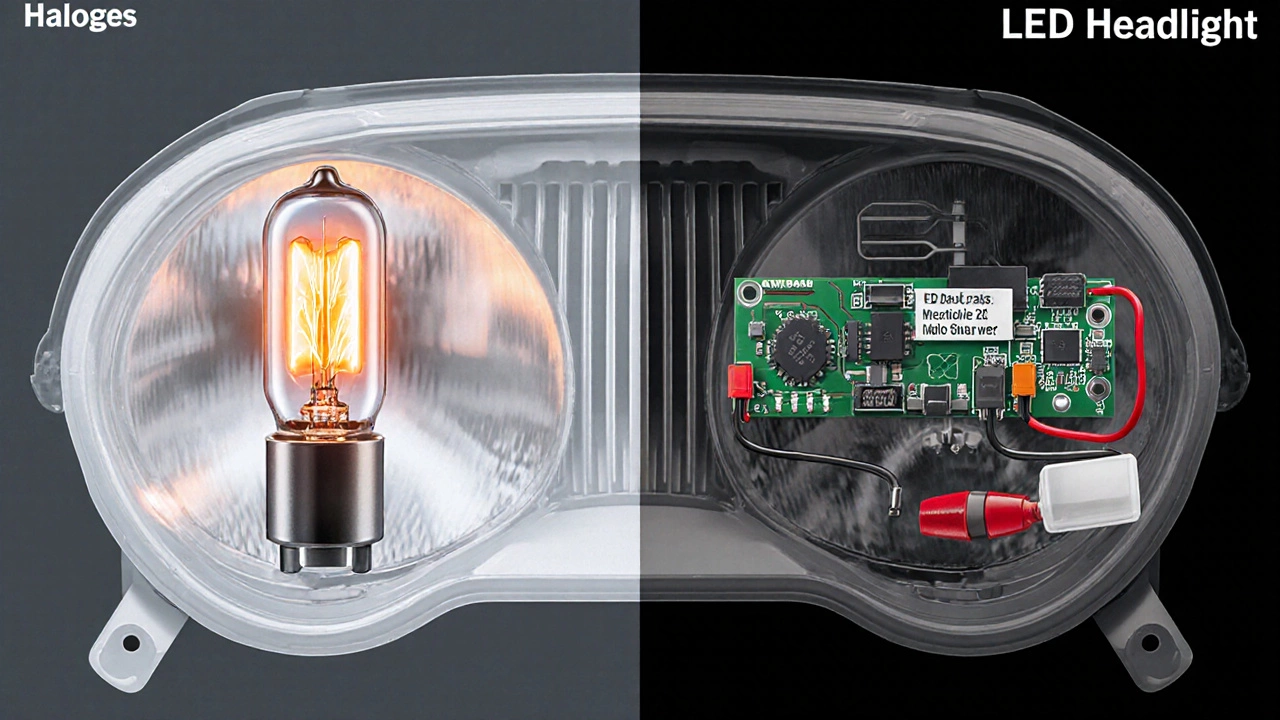
Legal and Safety Aspects of LED Swaps
In Australia, the Road Vehicles (Lighting) Regulations 2011 require headlights to meet specific luminous intensity and beam pattern standards. An LED that’s too bright or has an uneven distribution can cause glare, leading to a failed inspection.
Key legal checkpoints:
- Beam Pattern - LED modules must maintain a proper cutoff to avoid dazzling oncoming drivers. Projector lenses often need re‑aiming.
- Lumens Limit - Exceeding ~2,500 lumens per low beam can be considered illegal for passenger cars.
- Certification - Look for LEDs that carry a compliance mark (e.g., ECE R112) indicating they’ve passed tests.
Skipping these checks can lead to fines and a failed MOT.
Step‑by‑Step Guide to a Clean LED Swap
- Identify the Bulb Size - Check the owner’s manual or the existing bulb for codes like H7, H4, or HB3.
- Select a Certified LED Kit - Choose a reputable brand that lists lumen output, color temperature, and CANbus compatibility.
- Gather Additional Parts - Depending on your car, you may need a load resistor, CANbus decoder, or new heat‑sink brackets.
- Disconnect the Battery - Prevent accidental shorts while working on the headlight circuit.
- Remove the Old Halogen - Unclip the housing, twist the bulb counter‑clockwise, and pull it out.
- Install the LED - Insert the LED module, ensuring the base seats fully. If it feels loose, consider an adapter sleeve.
- Attach Any Resistors or Decoders - Connect the load resistor in parallel with the LED’s power wire, or plug the CANbus decoder into the socket.
- Reconnect the Battery and Test - Turn the lights on. Verify both low and high beams function, and check for warning symbols.
- Adjust the Aim - Use a flat wall at 25 ft to align the beam pattern. The low beam should produce a clear cutoff line.
- Secure Heat Management - If the LED gets hot, add a thermal pad or reposition the heat‑sink to keep temperatures below 80 °C.
Following these steps removes most guesswork and keeps you on the right side of the law.
Halogen vs LED: Quick Comparison
| Attribute | Halogen | LED |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Power | 55 W (H7) | 15‑30 W |
| Lumens | 1,200‑1,500 | 2,500‑4,000 |
| Color Temperature | 3,200‑3,400 K (warm white) | 5,000‑6,500 K (daylight) |
| Lifespan | ≈1,000 hours | ≈30,000 hours |
| Energy Consumption | High | Low |
| Heat Output | Very hot (risk of glass breakage) | Cooler, needs heat‑sink |
| CANbus Compatibility | Native | Often requires resistor or decoder |
| Cost (per pair) | $30‑$50 | $100‑$250 |

Common Pitfalls and Pro Tips
- Poor Fit - If the LED module won’t sit flush, try a low‑profile version or trim the housing gently (only if you know what you’re doing).
- Blinding Glare - Adjust the beam with a screwdriver on the adjustment screws near the housing. Aim at a wall and ensure the cutoff line is sharp.
- Battery Drain - Some cheap LEDs keep a tiny current flowing even when off, which can drain the battery over weeks. Choose a kit with a proper shutdown driver.
- Heat Buildup - Install thermal pads or silicone paste between the LED board and heat‑sink for better dissipation.
- Warranty Issues - Modifying the headlight system can void the vehicle’s warranty. Check the dealer policy before you start.
Bottom Line: Do You Need More Than a Simple Swap?
If your car uses a basic halogen system with a simple socket, a plug‑and‑play LED kit that includes a built‑in CANbus decoder may work straight out of the box. Most newer models, especially those with projector lenses or sophisticated CANbus monitoring, will require extra parts-load resistors, decoders, or even a professional re‑programming session.
In short, you can’t just yank out the old bulb and expect the LED to shine perfectly. Think of it as a mini‑upgrade project: choose the right size, add the needed electronics, respect legal limits, and you’ll gain brighter, whiter light plus long‑term energy savings.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will LED headlights work on any car that has halogen bulbs?
Not always. The LED must match the socket type (H7, H4, etc.) and the car’s CANbus system must be satisfied with a resistor or decoder. Some high‑tech vehicles also need beam‑pattern adjustments.
Do I need a separate power driver for LED headlights?
Most LED kits come with an integrated driver that regulates voltage. If you buy bare LED modules, you’ll need a dedicated driver to avoid flicker and protect the LEDs.
Can I use a cheap LED bulb and avoid CANbus errors?
Cheaper LEDs often lack built‑in CANbus compatibility, so you’ll likely see a warning light. Adding a load resistor or a small CANbus decoder usually solves the issue.
Are LED headlights legal in Australia?
Yes, provided they meet the ECE R112 standard for luminous intensity and have a proper beam cutoff. Always check the compliance label before fitting.
How much will a full LED headlight conversion cost?
A decent DIY kit runs $120‑$250 per pair, plus $20‑$40 for any needed CANbus decoder or load resistor. Professional installation can add $100‑$200.




